Last Updated on April 18, 2025 by SPOTKEYS
How to Merge Cells in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide for Microsoft Office Users
Merging cells in Microsoft Excel is a fundamental skill for creating organized, visually appealing spreadsheets. Whether you’re formatting reports, designing dashboards, or preparing data for presentations, merging cells can enhance clarity and professionalism. This guide is tailored for users of Microsoft Office and other Microsoft Office applications, providing practical steps, tips, and answers to common user questions. By mastering this feature, you can maximize the value of your Microsoft Office subscription and streamline your workflow.
Why Merge Cells in Excel?
Merging cells combines multiple cells into a single, larger cell, often used to:
- Create centered titles or headers across multiple columns.
- Improve the visual layout of tables or forms.
- Group related data for better readability.
This feature is available across Microsoft Office applications, including Excel for Microsoft 365, Excel 2019, Excel 2016, and older versions, making it accessible to all Microsoft Office users.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Merge Cells in Excel
Follow these practical steps to merge cells in Excel efficiently. These instructions apply to Microsoft Excel on Windows, macOS, and web versions.
Step 1: Select the Cells to Merge
- Open your Excel workbook in Microsoft Excel.
- Highlight the cells you want to merge. For example, to create a title spanning columns A1 to C1, click and drag to select A1:C1.
- Tip: Ensure the cells are adjacent (e.g., in a row or column). Non-adjacent cells cannot be merged.
Step 2: Access the Merge Option
- Navigate to the Home tab on the Excel ribbon.
- Locate the Alignment group.
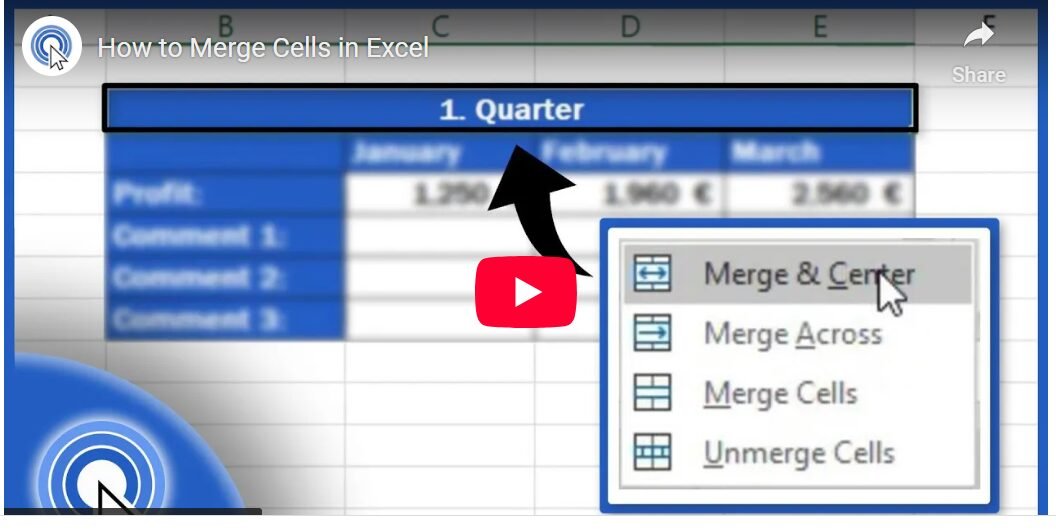
- Click the Merge & Center dropdown button to view merge options.
Step 3: Choose a Merge Option
Excel offers four merge options:
- Merge & Center: Combines selected cells into one and centers the content. Ideal for headers.
- Merge Across: Merges cells in each selected row separately (useful for row-based formatting).
- Merge Cells: Combines cells without centering the content.
- Unmerge Cells: Reverses a merge, splitting the cell back into individual cells.
Select Merge & Center for the most common tasks, such as creating a title.
Step 4: Verify and Format
- After merging, the content from the top-left cell is retained, and the other cell contents are deleted.
- Adjust font size, alignment, or cell borders in the Home tab to enhance the appearance.
- Note: Merged cells may affect sorting or filtering. Use them primarily for formatting, not data storage.
Tips for Merging Cells in Excel
- Use Keyboard Shortcuts: After selecting cells, press Alt + H + M + C to quickly apply Merge & Center (Windows only).
- Check Compatibility: Merging works consistently across Excel for Microsoft 365, desktop versions, and Excel Online, ensuring seamless collaboration.
- Avoid Over-Merging: Excessive merging can complicate data analysis or formulas. Reserve it for headers or labels.
- Backup Data: Since merging deletes content from all but the top-left cell, copy important data before merging.
Common User Questions Answered
To address the needs of Microsoft Office users, we’ve compiled answers to popular search queries (People Also Ask) related to merging cells in Excel.
1. What Happens When You Merge Cells in Excel?
When you merge cells, Excel combines the selected cells into one larger cell. Only the content in the top-left cell is preserved, and content in other cells is deleted. The merged cell adopts the formatting of the top-left cell. This feature is purely for formatting and does not affect calculations or data in other cells.
2. Can You Merge Cells Without Losing Data?
By default, merging cells deletes content from all but the top-left cell. To merge without losing data:
- Copy the content of the cells you want to merge.
- Paste it into the top-left cell or a separate location.
- Merge the cells using Merge & Center or Merge Cells.
- Manually re-enter or concatenate the data in the merged cell if needed.
Alternatively, use the CONCATENATE function or & operator to combine text before merging. For example: =A1&” “&B1 combines text from A1 and B1 with a space.
3. How Do You Unmerge Cells in Excel?
To unmerge cells:
- Select the merged cell.
- Go to the Home tab, click the Merge & Center dropdown, and choose Unmerge Cells.
- The cell splits back into its original grid, with the content placed in the top-left cell.
4. Why Can’t I Merge Cells in Excel?
Common reasons you can’t merge cells include:
- Protected Worksheet: If the sheet is protected, unprotect it via Review > Unprotect Sheet (password may be required).
- Table Format: Cells in an Excel Table (Insert > Table) cannot be merged. Convert the table to a range first (Table Design > Convert to Range).
- Non-Adjacent Cells: Only adjacent cells can be merged.
- Shared Workbook: Merging may be restricted in shared or co-authored workbooks.
Advanced Uses of Merging Cells for Microsoft Office Users
Microsoft Office buyers, including those using Microsoft 365 subscriptions, can leverage merged cells for advanced tasks:
- Creating Professional Reports: Use merged cells for titles in financial reports or project trackers.
- Designing Forms: Merge cells to create clean input fields in Excel-based forms.
- Building Dashboards: Combine merged cells with charts for visually appealing dashboards in Excel.
For users integrating Excel with other Microsoft Office applications:
- PowerPoint: Copy merged cells from Excel and paste them into PowerPoint slides for consistent formatting.
- Word: Embed Excel tables with merged cells into Word documents for professional reports.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Merged Cells Break Sorting/Filtering: Avoid merging cells in data ranges used for sorting or filtering. Instead, use Center Across Selection (Home > Alignment Settings) for visual centering without merging.
- Formatting Issues: If merged cells don’t display correctly, check cell alignment or adjust column widths.
- Excel Online Limitations: While Excel Online supports merging, some advanced formatting options may require the desktop app.
Why Microsoft Office is the Best Choice for Excel Users
Microsoft Office, particularly Microsoft 365, offers unmatched flexibility for Excel users. With regular updates, cloud integration, and cross-platform support, it ensures you can merge cells and perform other tasks seamlessly on Windows, macOS, iOS, or Android. users benefit from:
- Excel’s Robust Features: From merging cells to advanced formulas, Excel is a powerhouse for data management.
- Integration with Other Apps: Use merged cells in Excel alongside Word, PowerPoint, or Teams for cohesive workflows.
- Scalability: Microsoft 365 subscriptions cater to individuals, businesses, and enterprises, making it ideal for all users.
For pricing or subscription details, visit Microsoft’s official site.
Conclusion
Merging cells in Excel is a simple yet powerful way to enhance your spreadsheets’ readability and professionalism. By following this guide, Microsoft Office users can confidently merge cells, troubleshoot issues, and apply advanced formatting techniques. Whether you’re a Microsoft 365 subscriber or using a standalone Excel version, mastering this feature will elevate your productivity and make the most of your Microsoft Office investment.
Ready to explore more Excel features? Dive into Microsoft Office’s extensive tools and create stunning, efficient spreadsheets today!